Internet-
A means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers. When two computers are connected over the Internet, they can send and receive all kinds of information such as text, graphics, voice, video, and computer programs.No one owns Internet, although several organizations the world over collaborate in its functioning and development. The high-speed, fiber-optic cables (called backbones) through which the bulk of the Internet data travels are owned by telephone companies in their respective countries.
The Internet grew out of the Advanced Research Projects Agency's Wide Area Network (then called ARPANET) established by the US Department Of Defense in 1960s for collaboration in military research among business and government laboratories.
Later universities and other US institutions connected to it. This resulted in ARPANET growing beyond everyone's expectations and acquiring the name 'Internet.'The development of hypertext based technology (called World Wide web, WWW, or just the Web) provided means of displaying text, graphics, and animations, and easy search and navigation tools that triggered Internet's explosive worldwide growth.
A means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers. When two computers are connected over the Internet, they can send and receive all kinds of information such as text, graphics, voice, video, and computer programs.No one owns Internet, although several organizations the world over collaborate in its functioning and development. The high-speed, fiber-optic cables (called backbones) through which the bulk of the Internet data travels are owned by telephone companies in their respective countries.
The Internet grew out of the Advanced Research Projects Agency's Wide Area Network (then called ARPANET) established by the US Department Of Defense in 1960s for collaboration in military research among business and government laboratories.
Later universities and other US institutions connected to it. This resulted in ARPANET growing beyond everyone's expectations and acquiring the name 'Internet.'The development of hypertext based technology (called World Wide web, WWW, or just the Web) provided means of displaying text, graphics, and animations, and easy search and navigation tools that triggered Internet's explosive worldwide growth.
Connecting with mobile
Connecting with Computer Laptop / Desktop
Definition of 'URL'
A URL is an address that shows where a particular page can be found on the World Wide Web. URL is an abbreviation for 'Uniform Resource Locator'.
What Is a URL?
If you've been surfing the Web, you have undoubtedly heard the term URL and have used URLs to access HTML pages from the Web.
It's often easiest, although not entirely accurate, to think of a URL as the name of a file on the World Wide Web because most URLs refer to a file on some machine on the network. However, remember that URLs also can point to other resources on the network, such as database queries and command output.
Definition: URL is an acronym for Uniform Resource Locator and is a reference (an address) to a resource on the Internet.
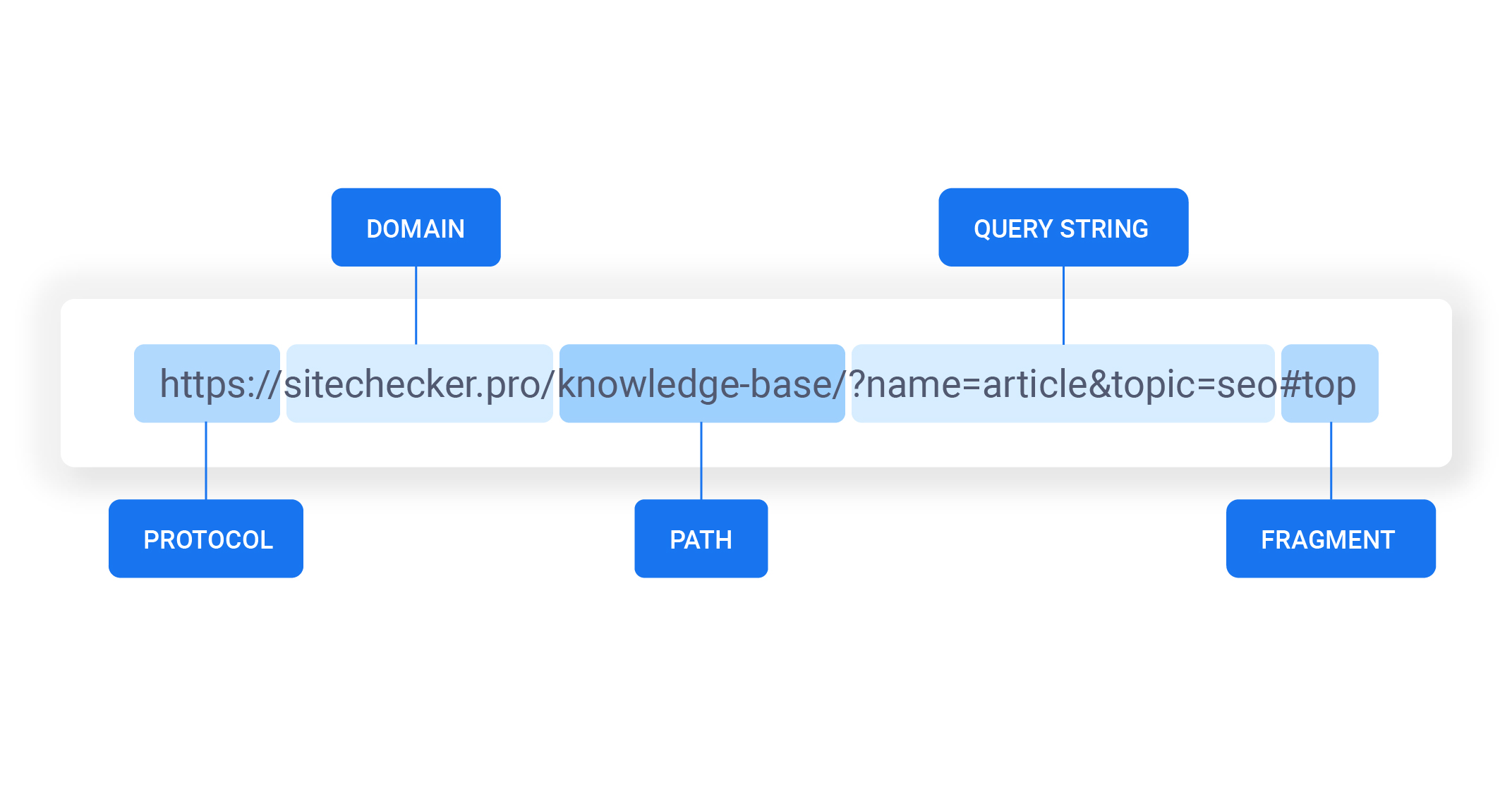
A URL has two main components:
The resource name is the complete address to the resource. The format of the resource name depends entirely on the protocol used, but for many protocols, including HTTP, the resource name contains one or more of the following components:
It's often easiest, although not entirely accurate, to think of a URL as the name of a file on the World Wide Web because most URLs refer to a file on some machine on the network. However, remember that URLs also can point to other resources on the network, such as database queries and command output.
Definition: URL is an acronym for Uniform Resource Locator and is a reference (an address) to a resource on the Internet.
- Protocol identifier: For the URL
http://example.com, the protocol identifier ishttp. - Resource name: For the URL
http://example.com, the resource name isexample.com.
The resource name is the complete address to the resource. The format of the resource name depends entirely on the protocol used, but for many protocols, including HTTP, the resource name contains one or more of the following components:
- Host Name
- The name of the machine on which the resource lives.
- Filename
- The pathname to the file on the machine.
- Port Number
- The port number to which to connect (typically optional).
- Reference
- A reference to a named anchor within a resource that usually identifies a specific location within a file (typically optional).
URL structure
URL address has a determined structure which includes:
- method of access to the resource that is also named the network protocol;
- access authorization;
- hosts – DNS address that is inscribed as IP address;
- port – one more obligatory detail included in combination with IP address;
- track – determines the information about the method of gaining access;
- parameter – the internal information of resource about the file.

Examples of friendly and non-friendly URL
The main part of the URL-address is the domain name of the website. To choose the proper one and thus to enable the effective site promotion in search systems, use our guide about domain name search before starting a business.
URL story
Like any other concept, the URL has its own story. Today its main function is to point out the terminal server where the information is stored. Created in 1990 by the acknowledged British inventor Sir Timothy John, the URL first was represented in Geneva. In the early days, it was used to determine the location of particular files on the Internet. But the developers came to the point that URL-address can serve to give the users access to other resources.







No comments:
Post a Comment